What Is Thermodynamics?
Thermodynamics is the science that studies how heat and energy move and change in the universe.
- It explains how heat flows from warmer things to cooler ones.
- The First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy cannot be created or destroyed — only changed (like from heat to motion).
Internal Energy (U): Energy stored in the movement of atoms and molecules of all substances
Formula: ΔU = Q − W
- ΔU = change in internal energy
- Q = heat added to the system
- W = work done by the system
How Heat Affects Our World
Thermodynamics helps explain real-world machines, weather, and even how your body works!
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics: Heat naturally flows from hot to cold, unless energy is added to reverse it.
- Real-World Examples:
- Your body uses thermodynamics to stay warm by shivering and cool down by sweating.
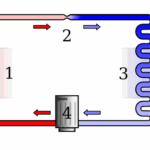
- Refrigerators: They use refrigerant fluid and a compressor to pull heat from the inside and release it outside.
- Charging a phone: Electrical energy is stored in the battery, but some is lost as heat, causing the phone to warm up.
Fun Facts
Here are some interesting facts about thermodynamics:
- Black holes follow the laws of thermodynamics, too!
- A microwave heats food using radiation, causing water molecules to vibrate and create heat from the inside out!
- Car engines turn only about 30% of fuel energy into motion—the rest is lost as heat!
- The coldest possible temperature, absolute zero (–273.15°C), is when particles stop moving completely!
Review
Let’s quickly recap what we learned about the basics of thermodynamics:
- What law says energy cannot be created or destroyed? First Law of Thermodynamics
- What do fridges move out to keep things cold? Heat
- What is the energy stored in the movement of atoms and molecules? Internal Energy
- What does the Second Law of Thermodynamics say about how heat flows? From Hot to Cold

Recent Comments