What Is a Chemical Equation?
Chemical equations are like recipes that show what goes into a chemical reaction and what comes out.
- A chemical reaction is when substances change into something new (like baking a cake).
- A chemical equation shows this change using chemical formulas and symbols.
- Example: H2+O2→H2O (hydrogen + oxygen = water.)
- The arrow (→) means “yields” or “produces.”
-
- The small numbers written after chemical symbols are called subscripts.
-
- They show how many atoms of each element are in a molecule.
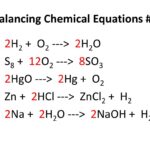
Why Do We Balance Equations?
Balancing chemical equations follows the rule that matter can’t be created or destroyed — just rearranged.
- Every atom on the left (reactants) must appear on the right (products).
- That’s why we balance chemical equations: to show the Law of Conservation of Mass.
- Example: H2+ ½ O2 → H2O or 2H2 + O2→ 2H2O
- Coefficients (big numbers in front) are used to balance equations, not subscripts!
Fun Facts
Here are some interesting facts about chemical equations:
- Antoine Lavoisier, the “father of modern chemistry,” helped create the rules for balancing equations.
- Different metal salts in the equations create colors, like strontium for red and copper for blue.
- Your body runs thousands of tiny chemical equations every second to keep you alive.
- Photosynthesis is a chemical equation that plants use to convert sunlight into energy!
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Review
Let’s quickly recap what we learned about chemical equations:
- What does a chemical equation describe? A Chemical Reaction
- What law must we follow when balancing chemical equations? Law of Conservation of Mass
- What symbol separates reactants from products? An Arrow
- What do we use to balance equations? Coefficients

Recent Comments