What Is Cellular Respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert food into usable energy, breaking down glucose (sugar) in the presence of oxygen to release energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
Three Stages of Cellular Respiration:
- Glycolysis: Occurs in the cytoplasm; glucose is broken down into smaller molecules, producing a small amount of ATP.
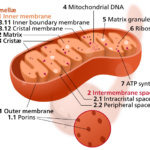
- Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): Happens in the mitochondria; releases CO₂ and produces high-energy molecules (NADH, FADH₂).
- Electron Transport Chain: Occurs in the mitochondria; uses oxygen to generate most of the ATP.
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy (ATP)
Importance of Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is vital for powering every process in living organisms.
- Energy for Life: ATP fuels essential activities like muscle movement, cell repair, and brain function.
- Oxygen’s Role: Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, enabling maximum ATP production.
- In Plants and Animals: Both plants and animals perform cellular respiration to break down sugars for energy.
Without ATP, cells cannot maintain their structure or pump out toxins, leading to swelling, damage to cell membranes, and eventual cell death.
Fun Facts
Here are some interesting facts about about cellular respiration:
- Your body produces and uses its weight in ATP every day!
- Mitochondria, where most cellular respiration happens, are known as the “powerhouses” of the cell.
- When your muscles experience intense activity with limited oxygen, they switch to anaerobic respiration, producing lactic acid, which can cause muscle cramps.
- Cyanide is deadly because it blocks the electron transport chain, stopping ATP production.
Review
Let’s quickly recap what we learned about cellular respiration:
- What is the main product of cellular respiration? ATP
- Which gas is essential for the electron transport chain? Oxygen
- Where does glycolysis occur? Cytoplasm
- Which organelle is the powerhouse of the cell? Mitochondria

Recent Comments