How Solar Panels Work
Solar panels capture sunlight and transform it into usable electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
- Solar panels consist of many solar cells, which are usually made from silicon, a material that easily moves electrons.
- When sunlight hits these cells, the energy knocks electrons from atoms inside the silicon.
- This movement of electrons creates an electric current — this is how electricity is formed.
- Wires then carry this electric current away from the panel to power devices.
Yes, solar panels can even power entire cities when installed at a large scale in solar farms and connected to the grid!
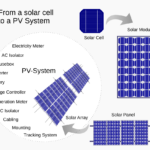
The Parts of a Solar Energy System
A solar energy system needs more than just panels to bring sunlight to your plug.
- Solar panels collect sunlight and start the electricity process.
- Inverters change the electricity from DC (direct current) to AC (alternating current), which is used in homes.
- Batteries can store extra electricity at night or during cloudy days.
- Meters and controllers manage how much electricity is made and how it flows through the system.
Combining these parts allows solar panels to provide clean power beyond a single home—when scaled up, they can support neighborhoods or cities.
Fun Facts
Here are some interesting facts about solar power:
- The sun sends more energy to Earth in one hour than humans use in a whole year.
- The International Space Station uses solar panels to stay powered in orbit.
- Solar-powered cars, boats, and even airplanes have been built.
- The first solar cell was invented in 1954 and was used in space missions.
Review
Let’s quickly recap what we learned about solar power:
- What type of current do solar panels produce? DC
- What material is commonly used in solar cells? Silicon
- What device changes DC to AC electricity? Inverter
- What process starts when sunlight hits a solar cell? Photovoltaic

Recent Comments