The Basics of the Nitrogen Cycle
The nitrogen cycle is nature’s way of making nitrogen useful for living things.
What is Nitrogen?
- Nitrogen is a gas that makes up 78% of the air we breathe, but it must be converted into different forms to be useful to plants and animals.
The Role of the Nitrogen Cycle:
- It moves nitrogen between the air, soil, plants, animals, and back to the air.
Why It’s Important: Nitrogen is essential for life because it is a key component of DNA, proteins, and chlorophyll. Without nitrogen, plants, animals, and humans cannot grow or reproduce.
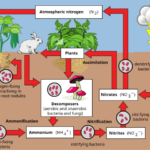
Key Steps in the Nitrogen Cycle
- The nitrogen cycle ensures that this essential element is reused in ecosystems.
- Nitrogen Fixation: Bacteria in soil or lightning convert nitrogen gas (N₂) into forms like ammonia (NH₃) that plants can use.
- Nitrification: Soil bacteria convert ammonia into nitrites (NO₂⁻) and nitrates (NO₃⁻), which plants absorb.
- Assimilation: Plants take in nitrates to grow and create proteins, while animals get nitrogen by eating plants or other animals.
- Ammonification: When plants and animals die or release waste, decomposers like bacteria break down organic material, returning ammonia to the soil.
- Denitrification: Other bacteria convert nitrates back into nitrogen gas (N₂), which returns to the atmosphere.
Fun Facts
Here are some interesting facts about Nitrogen:
- Only a few types of bacteria can “fix” nitrogen from the air—without them, plants wouldn’t survive!
- Lightning strikes convert nitrogen gas into a form plants can use, creating millions of tons of nitrogen compounds globally yearly.
- Nitrogen is a key ingredient in fertilizers that help grow our food.
- Too much nitrogen in water can lead to “dead zones,” where fish and other marine life can’t survive.
Review
Let’s quickly recap what we learned about the Nitrogen Cycle:
- What step involves bacteria converting nitrogen gas (N₂) into ammonia (NH₃)? Fixation
- What process converts ammonia into nitrates (NO₃⁻) that plants can absorb? Nitrification
- What is the process by which decomposers return nitrogen to the soil as ammonia? Ammonification
- What step releases nitrogen gas back into the atmosphere? Denitrification

Recent Comments