Speed & Velocity
Speed tells how fast something moves, while velocity adds direction to that motion.
Speed:
- Distance traveled over time (e.g., 60 miles per hour).
- Formula: Speed = Distance ÷ Time
- Units: meters per second (m/s), kilometers per hour (km/h), miles per hour (mph).
Velocity:
- Speed with direction (e.g., 500 km/h north).
- Changes in velocity occur when speed or direction changes.
Acceleration
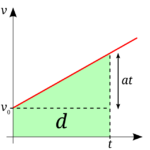
Acceleration is the change in speed or direction of an object over time.
Formula: Acceleration = Change in Velocity ÷ Time
Units: meters per second squared (m/s²).
Types of Acceleration:
- Positive Acceleration: Object is speeding up. Example: A car going from 0 to 60 mph in 6 seconds.
- Negative Acceleration (Deceleration): Object is slowing down. Example: A bike braking at a stoplight.
- Directional Acceleration: Object changes direction while moving. Example: A rollercoaster turning sharply.
Practical Applications
Understanding speed, velocity, and acceleration helps us in everyday life and various fields.
Cars and Safety: Speedometers and GPS systems help monitor speed and velocity for safe driving.
Sports: Athletes train to optimize their acceleration and velocity for better performance (e.g., sprinters).
Space Exploration: Rockets need precise calculations of speed and acceleration to launch, orbit, and land safely on other planets.
Technology and Gadgets: Sensors in smartphones, cars, and drones use acceleration data for navigation and stabilization.
Fun Facts
Here are some interesting facts about speed, velocity & acceleration:
- The cheetah, the fastest land animal, can accelerate from 0 to 60 mph in just 3 seconds!
- Earth spins on its axis at about 1,000 mph and travels around the sun at 67,000 mph—talk about speed!
- Acceleration due to gravity on Earth is 9.8 m/s², which means every second an object falls, its velocity increases by 9.8 m/s.
- Formula 1 race cars can accelerate from 0 to 100 mph in under 3 seconds, showcasing extreme acceleration and velocity control.
Review
Let’s quickly recap what we learned about speed, velocity & acceleration:
- What is the formula for speed? Distance ÷ Time
- How is velocity different from speed? Direction
- What is the formula for acceleration? Change in Velocity ÷ Time
- What’s an example of acceleration that doesn’t involve speeding up? Changing Direction

Recent Comments