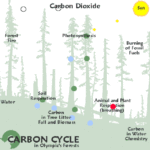
What Is the Carbon Cycle?
The carbon cycle describes how carbon moves through the Earth’s systems
Key Steps in the Carbon Cycle:
Photosynthesis: Plants take in carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the air and convert it into oxygen and sugars.
Respiration: Animals release CO₂ back into the air when they breathe.
Decomposition: Dead plants and animals release carbon into the soil and atmosphere as they break down.
Ocean Absorption: Oceans absorb CO₂ from the atmosphere, storing it in water and marine organisms.
Climate Change Connection
Electricity and magnetism are fundamentally two aspects of the same phenomenon, called “electromagnetism.”
How It Works:
Human activities are upsetting the natural carbon balance, leading to climate change.
Burning Fossil Fuels: Releases large amounts of CO₂ into the atmosphere, trapping heat and warming the planet.
Deforestation: Reduces the number of trees available to absorb CO₂.
Methane (CH₄): A powerful greenhouse gas that agriculture (e.g., cows) and landfills release.
Effects of Excess Carbon:
- Rising global temperatures.
- Melting ice caps and rising sea levels.
- More extreme weather events, like hurricanes and droughts.
Fun Facts
Here are some interesting facts about about the carbon cycle and climate change:
- The Amazon rainforest absorbs about 2 billion tons of CO₂ each year!
- Volcanic eruptions naturally release CO₂, but humans release 100 times more CO₂ than volcanoes annually.
- Oceans hold 50 times more carbon than the atmosphere!
- The oldest carbon on Earth is trapped in rocks over 3 billion years old.
Review
Let’s quickly recap what we learned about the carbon cycle and climate change:
- What do humans burn that releases CO₂? Fossil Fuels
- What process removes CO₂ from the atmosphere? Photosynthesis
- What type of gas traps heat in the atmosphere? Greenhouse
- Which natural system absorbs the most carbon? Oceans

Recent Comments