What is Quantum Physics?
Quantum physics is a branch of science that studies the smallest particles in the universe, such as atoms, and subatomic particles, like electrons and photons.
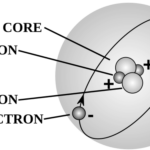
- Atoms: The basic building blocks of matter, consisting of a nucleus (protons and neutrons) and electrons that orbit around the nucleus.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that move around the nucleus of an atom.
- Protons and Neutrons: Particles found in the nucleus; protons have a positive charge, and neutrons have no charge.
Wave-Particle Duality:
Particles like electrons and photons can behave both as particles and waves. They can spread out like waves and also be counted like particles.
Key Concepts Of Quantum Physics
- Quantization of Energy:
Energy is not continuous but comes in small, discrete units called “quanta.” For example, light comprises particles called photons, each carrying a specific amount of energy.
- Superposition:
Particles can exist in multiple states until they are measured. For example, an electron can be in two places at once.
- Uncertainty Principle:
It is impossible to know both the exact position and exact momentum of a particle at the same time.
Study of Small Particles
Scientists have cool ways to study particles that are too small to be seen with our eyes.
Electron Microscopes: These microscopes use electrons (tiny particles) to create super-detailed images of small things instead of light.
Particle Accelerators: These huge machines speed up tiny particles and crash into each other. Scientists study the pieces that come out of these crashes to learn about the smallest building blocks of everything.
Spectroscopy: Scientists use light to study particles. By shining light on a particle and observing how it reacts, they can learn what it’s made of.
Fun Facts
Here are some interesting facts about Quantum Physics:
- When two particles become entangled, the state of one instantly affects the state of the other, no matter how far apart they are. Einstein called this “spooky action at a distance.”
- Unlike classical computers that use bits (0 or 1), quantum computers use qubits, which can be both 0 and 1 at the same time, allowing them to solve certain problems much faster.
- Quantum mechanics explains the emission of photons, which is the fundamental principle behind lasers. Lasers are used in various applications, from medical surgeries to barcode scanners.
Review
Let’s quickly recap what we learned about the basics of Quantum Physics:
- What are the three main subatomic particles in an atom? Protons, Neutrons & Electrons
- What is the smallest unit of energy called? A Quantum
- What is it called when particles can exist in multiple states at once? Superposition
- How does light behave according to quantum physics? Wave & Particle

Recent Comments