Guiding Questions
- What is the integumentary system?
- What are the components of the integumentary system?
- What are the functions of the integumentary system?
- What are some common diseases related to the integumentary system?
Overview
When you look at the parts of an egg, you can notice that there are 2 main parts – the outer shell and the inner contents (the egg white and yolk). The shell is very important in protecting the inner contents of the egg. It’s also important for structural purposes.
In a way, this is how our integumentary system works. It consists of the skin, nails, hair, and glands that act as the body’s first layer of defense from physical harm, UV radiation, and more.
The Parts of the Integumentary System
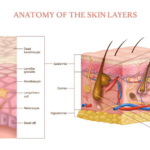
The skin is actually the largest organ of your body! Within this 2 mm thick barrier, there are 3 very important layers:
- The epidermis is the very top layer. It’s the part that gives your skin its color; it’s also the part you touch whenever something comes in contact with you. In addition, it is a protective layer for the body.
- The dermis is the thick, middle layer sandwiched between the epidermis and hypodermis. It contains things like glands (that secrete oil and sweat) along with hair follicles.
- The hypodermis is the fatty tissue that insulates your body. It is the very bottom (innermost) layer of the skin.
When you look at the nails on the tips of the fingers and toes, they look relatively simple. However, in reality there are quite a few parts of those seemingly simple components of the body.
- Nail plate: This is the part of the nail that is able to be seen.
- Nail bed: This is the skin that is directly under your nail plate.
- Cuticle: The cuticle is the small skin layer at the bottom of your nail.
- Matrix: This is where the nail grows from.
- Lunula: This is the lighter (white) colored curve at the bottom of your nail.
There are 3 main parts of the hair.
- The hair grows from the hair bulb under your skin.
- The hair follicle is the tube that keeps the hair in the skin.
- Lastly, the hair shaft is the part of the hair you can see located above the skin.
The nerves are what help you feel things like touch, pain, and even temperature. They are located throughout your body. Whenever you come into contact with something, they send signals to the brain. The nerves are technically a part of the nervous system, but they work closely with the integumentary system.
Lastly, there are a few different glands that your integumentary system includes.
- Sudoriferous (sweat) glands: These are the glands that release sweat from your skin.
- Sebaceous glands: These glands produce oil called sebum all over the body that help moisturize and protect the hair and skin.
- Ceruminous glands: Ceruminous glands are responsible for producing ear wax in the ears.
- Mammary glands: These are the glands in the chest. These are the glands that produce milk after females give birth to help provide nutrients to their young. They are truly modified sweat glands.
Integumentary System Functions
The integumentary system is vital for a few different things.
First of all, it acts as the first line of defense. It protects the inner contents of the body and makes sure that any harmful particles can’t get in.
It is also responsible for healing wounds whenever your body incurs physical injury. This includes bleeding, clotting, the actual healing process, and sometimes scarring.
When the skin is exposed to the UV rays of the sun, it is able to produce vitamin D that can be used by the body.
Finally, nerves in the integumentary system help you feel texture and pain. They give you the sensation of touch which allows you to feel contact, temperature, and pain.
Common Diseases
A few things can happen to your skin depending on different conditions.
You can get allergies on your skin from certain things. A common allergy is from plants like poison ivy and poison oak, which irritate the skin. Other things that can irritate your skin are bug bites.
Blisters, scars, wounds, burns, infections, rashes, etc. can all occur during traumatic events to the skin.
Your skin can also get a form of skin cancer called melanoma. This is when the uncontrolled division of skin cells creates a rapid-spreading cancerous tumor.
Some sensitive skin can experience dryness, acne, eczema, and other things.
Lastly, your skin can have some usually harmless skin lesions. Examples include moles and freckles. Although usually harmless, it’s always good to check them with your doctor to be safe.
Other things you can do to protect your skin are to wear sunscreen, avoid excessive radiation, and to use safe and healthy skincare.
Review
- How many layers of the skin are there? Three
- What is the topmost layer of your skin called? The Epidermis
- What is the skin directly under the nail plate? The Nail Bed
- How many parts of the hair are there? Three
- Which glands produce sweat? Sudoriferous (Sweat) Glands
- Which glands produce sebum (oil)? Sebaceous Glands

Recent Comments