The Science of Earth’s Heat
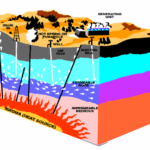
Geothermal energy is possible because the Earth’s core is incredibly hot, and that heat is constantly transferred outward through the crust.
- Source of Heat: The Earth’s core is as hot as the sun’s surface (5,500°C), primarily due to leftover formation heat and radioactive decay.
- Heat Transfer: This heat warms the magma (molten rock) and crust, naturally traveling outward.
- The Reservoir: In “hot spots” (near plate boundaries), water seeps down and turns into pockets of superheated steam or hot water.
- Depth: We only need to drill a few kilometers to tap into these steam reservoirs.
From Steam to Socket
High-pressure steam spins a turbine connected to a generator, creating electricity.
- Drilling: Wells are drilled deep into the Earth to reach the natural steam or hot water reservoirs.
- Extraction: The high-pressure steam naturally rushes up the well, carrying extreme amounts of heat energy with it.
- Turbine: The powerful rush of steam is directed onto the blades of a turbine, causing it to spin at high speed.
- Generation: The spinning turbine is connected to a generator, which converts that mechanical motion into electrical energy.
- Sustainability: Cooled water is reinjected to be naturally reheated, creating a continuous cycle.
Fun Facts
Here are some interesting facts about geothermal energy:
- Ancient Romans and Native Americans used hot springs for bathing, cooking, and heating.
- The country of Iceland uses geothermal energy for nearly 100% of its space heating and for about 30% of its electricity, thanks to its location on a volcanic fault line.
- Geothermal plants are built directly on top of or very close to a usable heat reservoir, which is why it’s not used everywhere.
- Yellowstone’s geysers are natural “pressure cookers” powered by geothermal heat.
Review
Let’s quickly recap what we learned about geothermal energy:
- What is the primary source of geothermal energy? Earth’s Core
- What is the superheated water or rock deep underground called? Reservoir
- What is the molten rock that transfers heat upward called? Magma
- What piece of equipment does the steam spin to generate power? Turbine

Recent Comments