How Are Plants Classified?
Scientists group plants based on their physical traits and evolution over time.
- Plant classification is part of taxonomy, the science of naming and organizing life.
- Main plant categories (from broad to specific):
Kingdom → Division → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
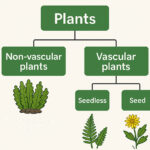
- Two major groups of plants:
🔸 Non-vascular plants: no tubes for water movement (e.g., mosses)
🔸 Vascular plants: have xylem and phloem to transport water/nutrients
- Vascular plants are further divided into:
🔹 Seedless (e.g., ferns)
🔹 Seed plants
Evolutionary Relationships Among Plants
Plants evolved over millions of years, gaining features like seeds, flowers, and fruits to survive better.
- Non-vascular plants (mosses, liverworts) appear first and need moist environments.
- Seedless vascular plants (ferns) have roots and tubes but reproduce by spores.
- Gymnosperms (pines, firs) have seeds in cones, no flowers.
- Angiosperms (roses, sunflowers, trees):
🔹 Most evolved group
🔹 Have flowers to attract pollinators
🔹 Produce fruits to protect and spread seeds
- Evolutionary trees (called cladograms) show how plants are related by common ancestors.
Fun Facts
Here are some interesting facts about plants:
- There are over 390,000 known species of plants!
- Banana plants are actually giant herbs, not trees!
- Some carnivorous plants like Venus flytraps are angiosperms!
- The cactus is a flowering plant, even though it rarely blooms.
- Algae aren’t classified as true plants, even though they do photosynthesis.
Review
Let’s quickly recap what we learned about plant classification:
- What type of plant produces cones? Gymnosperm
- What part of a plant helps attract pollinators? Flower
- What do ferns use to reproduce? Spores
- What is the most advanced plant group? Angiosperm

Recent Comments