Understanding Natural Selection
Natural selection is a process where organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring.
Key Components:
- Variation: Individuals in a species show differences in their traits.
- Inheritance: Some traits are passed from parents to offspring.
- Selection: Certain traits improve survival and reproduction chances.
- Time: Over generations, beneficial traits become more common.
Example: The peppered moth in England changed color from light to dark due to industrial pollution.
Charles Darwin’s Contribution
Charles Darwin was the pioneer of the Evolutionary Theory.
- He was an English naturalist who proposed the theory of evolution by natural selection.
- From 1831 to 1836, Darwin traveled worldwide, observing diverse flora and fauna.
- Darwin observed diverse species during his journey to the Galápagos Islands and noted variations that led to his groundbreaking ideas.
- In 1859, he published “On the Origin of Species,” detailing his theory and evidence for evolution.
Fun Facts
Here are some interesting facts about natural selection and Charles Darwin:
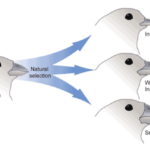
- Darwin noted that finches on different islands had varying beak shapes adapted to their specific food sources.
- Darwin hesitated for over 20 years to publish his theory, fearing public and scientific backlash.
- “Survival of the Fittest”: Philosopher Herbert Spencer coined this phrase, which is often associated with Darwin.
- Darwin’s work laid the foundation for modern evolutionary biology.
Review
Let’s quickly recap what we learned about natural selection and Charles Darwin:
- What is it called when individuals in a species show differences in their traits? Variation
- What was the name of Darwin’s famous book published in 1859? On the Origin of Species
- Which group of birds did Darwin study that helped him develop his theory of evolution? Finches
- What is it called when traits are passed from parents to offspring? Inheritance

Recent Comments