The Endocrine System – An Overview
The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce and release hormones to regulate vital body functions.
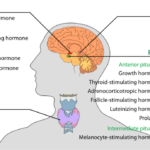
Pituitary Gland: The “master gland” controls growth and other glands.
Thyroid Gland: Regulates metabolism and energy.
Pancreas: Controls blood sugar levels with insulin and glucagon.
Adrenal Glands: Produces adrenaline and cortisol, which are crucial for stress response.
How Hormones Work:
Hormones are chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream to specific target organs.
They help maintain homeostasis—keeping the body in balance.
Hormones in Action
Hormones are precise messengers, targeting specific cells to perform vital functions.
Hormone-Receptor Interaction:
Hormones travel through the bloodstream and bind to specific receptors on target cells, like a key fitting into a lock.
Target Cells:
Only cells with the correct receptors respond to the hormone. For example, Insulin binds to receptors on muscle and liver cells to regulate blood sugar.
Hormonal Imbalance: Too much or too little hormone production can lead to issues like diabetes, thyroid disorders, or growth problems.
Fun Facts
Here are some interesting facts about hormones:
- The human body has over 50 different hormones.
- Melatonin helps animals hibernate, and humans adjust to jet lag.
- Adrenaline can make you temporarily stronger in emergencies.
- Laughing can boost endorphins, your body’s “feel-good” hormones.
- Oxytocin is called the “cuddle hormone” because it strengthens social bonds.
Review
Let’s quickly recap what we learned about hormones and the endocrine system:
- What is the “master gland” of the endocrine system? Pituitary
- Which hormone regulates blood sugar levels? Insulin
- Which gland controls metabolism? Thyroid
- What hormone is responsible for the fight-or-flight response? Adrenaline

Recent Comments