What Are Genetic Mutations?
Genetic mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can impact traits in various ways.
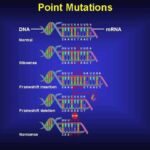
Types of mutations:
- Point Mutation: A single base change (e.g., sickle cell anemia).
- Deletion/Insertion: Adding or removing DNA bases.
- Frameshift Mutation: Alters the entire reading frame of DNA.
Causes of mutations:
- Spontaneous errors during DNA replication.
- Environmental factors like radiation, chemicals, and UV light.
Mutations can be silent (no effect), harmful (cause disease), or beneficial (lead to advantageous traits).
Helpful and Harmful Mutations
Mutations can drive evolution or lead to challenges—nature’s double-edged sword.
Helpful Mutations:
- Enable antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
- Create beneficial traits in evolution, such as longer necks in giraffes.
- Provide resistance to diseases like HIV in some humans.
Harmful Mutations:
- Cause genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis or Huntington’s disease.
- Lead to cancers due to DNA damage.
- Disrupt normal protein function.
Neutral Mutations: Have no noticeable effect on the organism.
Using Mutations in Science
Mutations are powerful tools that help scientists unlock the secrets of genes and develop life-saving treatments.
Studying Genes:
Scientists intentionally induce mutations in organisms like bacteria, mice, or plants to study how specific genes work.
Creating Medicines:
Mutations in DNA help identify genes linked to diseases, such as BRCA genes for breast cancer.
Scientists design medicines or treatments targeting the effects of harmful mutations (e.g., gene therapy).
Drug Development: Mutations in bacteria are used to study antibiotic resistance, leading to new drugs to combat superbugs.
Fun Facts
Here are some interesting facts about genetic mutations:
- Humans have about 60 new mutations in their DNA that their parents didn’t have.
- The gene for blue eyes is a mutation that occurred thousands of years ago.
- Some mutations allow certain animals, like Arctic foxes, to survive in extreme environments.
- Scientists use mutagenesis (inducing mutations) to create crops resistant to pests or harsh climates.
Review
Let’s quickly recap what we learned about genetic mutations:
- What are changes in the DNA sequence called? Mutations
- What type of mutation alters the reading frame of DNA? Frameshift
- What type of mutation involves a single base change, as seen in sickle cell anemia? Point
- What environmental factors can cause mutations? Radiation, Chemicals, UV Light

Recent Comments