The Science Behind Electricity
Electricity is the flow of electrons (tiny particles in atoms) through a conductor like a wire. Example: Batteries and power outlets provide electricity.
Current Types:
- Direct Current (DC): Flows in one direction (e.g., batteries).
- Alternating Current (AC): Changes direction constantly (e.g., power in homes).
Circuits: A complete path is needed for electricity to flow, like in a flashlight.
- Open Circuit: No flow of electricity.
- Closed Circuit: Electricity flows.
Conductors and Insulators: Materials like metals conduct electricity, while rubber and plastic stop it.
Magnetism & The Connection to Electricity
Electricity and magnetism are fundamentally two aspects of the same phenomenon, called “electromagnetism.”
How It Works:
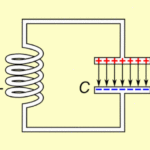
Moving electric charges produce a circular magnetic field.
Changing magnetic fields can induce electric currents.
Electromagnets:
Wrapping a wire carrying current around a metal core (like iron) creates an electromagnet.
Generators convert motion into electricity using magnets.
Electromagnets can be turned on and off by controlling the flow of electricity.
Electricity & Magnetism in Daily Life
From our homes to hospitals, electricity, and magnetism power it all!
Powering Devices: Electricity and magnetism work together in electric motors to power fans, refrigerators, and washing machines.
Communication Technology: Electromagnetic waves enable radios, televisions, and mobile phones to transmit signals.
Transportation: Trains use electromagnets in maglev (magnetic levitation) systems for smooth and fast travel.
Healthcare: MRI machines use magnets to create detailed images of the inside of our bodies.
Fun Facts
Here are some interesting facts about electricity & magnetism:
- Earth is a giant magnet with a magnetic field that protects us from solar radiation.
- Electromagnets are used in cranes to lift heavy scrap metal.
- Lightning is a natural example of electricity in action.
- Magnets lose their magnetic properties if heated above a specific temperature (called the Curie point).
Review
Let’s quickly recap what we learned about electricity & magnetism:
- What flows in an electric circuit? Electrons
- What is created when electricity flows through a wire? Magnetic Field
- What natural force protects Earth from solar radiation? Magnetism
- Which device converts motion into electricity? Generator

Recent Comments