First Line of Defense
The immune system’s first line of defense relies on physical and chemical barriers to prevent harmful pathogens from entering the body.
- Skin: Acts as a tough, protective outer layer, preventing most germs from entering the body.
- Mucus Membranes: Found in the nose, mouth, throat, and respiratory tract, they trap dust, bacteria, and viruses, preventing them from reaching deeper tissues.
- Saliva: Contains enzymes that help destroy bacteria in the mouth.
- Stomach Acid: Extremely acidic (pH around 1.5 to 3.5), killing most swallowed pathogens.
Second Line of Defense
The second line of defense springs into action when pathogens bypass physical and chemical barriers to stop the invaders.
Innate Immune System:
- It provides a non-specific defense, meaning it attacks any pathogen, not just a specific one.
- Acts immediately after detecting an invader.
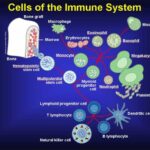
White Blood Cells (WBCs):
- Phagocytes (like macrophages and neutrophils) engulf and destroy harmful bacteria and viruses through phagocytosis.
- Natural Killer (NK) Cells attack and destroy infected or cancerous cells.
The Adaptive Immune System
The adaptive immune system specifically targets the type of germ causing the infection.
- B-cells produce antibodies that bind to and neutralize pathogens.
- T-cells destroy infected cells and signal other immune responses.
Memory Cells:
- After fighting an infection, memory cells “remember” the pathogen.
- This provides immunity, helping you fight the same pathogen faster in the future.
Vaccines: Teach the immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens without causing illness.
Fun Facts
Here are some interesting facts about the immune system:
- Your body produces around 1 million new white blood cells every second!
- Fever is your body’s way of creating an environment where germs can’t survive.
- The gut contains about 70% of your immune system.
- The largest organ of the immune system is the skin, which acts as a physical barrier.
- Sneezing helps expel germs and prevent them from entering deeper into your body.
Review
Let’s quickly recap what we learned about the immune system:
- What is the first line of defense in the immune system? Physical & Chemical Barriers
- Which cells produce antibodies? B-cells
- What type of immunity involves memory cells? Adaptive Immunity
- What kind of immunity provides a rapid, non-specific response to invaders? Innate Immunity

Recent Comments